InnSync User Guide
Welcome to the InnSync User Guide
Welcome to the InnSync User Guide – your essential companion for managing contacts and visitor information efficiently. Designed specifically for AirBnB owners.
In this comprehensive user guide, we will take you to experience a full journey with InnSync step by step.
Table of Contents
- 4.1 Command Summary
- 4.2 Features Related to Visitors
- 4.3 Features Related to Starring Visitors
- 4.4 Features Related to Tagging Visitors
- 4.5 Features Related to Requests
- 4.6 Adding a Memo to a Visitor
- 4.7 Features Related to Finding
- 4.8 General Features
- 4.9 Saving the Data
- 4.10 Editing the Data File
1. Introduction
1.1 What Is InnSync
InnSync is a desktop application designed specifically for managing contacts for AirBnB owners, optimized for use via a Command Line Interface (CLI) while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI). If you can type fast, InnSync can get your contact management tasks done faster than traditional GUI apps.
Key Features:
- Contact & Visitor Management: Add, edit, and delete contacts with ease.
- Rapid Command Execution: Quickly execute commands using a straightforward CLI.
- Automatic Data Persistence: Your changes are saved automatically to ensure all visitor details remain current.
1.2 User Proficiency and Expectations
Technical Skills: InnSync is designed for users with basic command line experience and familiarity with file navigation.
Efficiency: Built for AirBnB owners, the tool prioritizes quick, streamlined workflows to manage visitor and contact information.
User-Friendly: Whether you're new to command line tools or an experienced user, InnSync’s design caters to a broad range of technical proficiencies.
1.3 Why This Guide Matters
This guide is crafted to help you fully leverage InnSync’s features. As an AirBnB owner, managing visitor details quickly and accurately is vital. This guide provides clear instructions, examples, and troubleshooting tips so you can optimize your workflow and focus on delivering a great visitor experience.
2. How to Use This User Guide
This section explains how to navigate the guide and locate the information you need.
2.1 Navigating the Document:
- Table of Contents: Use the Table of Contents at the start to jump directly to sections relevant to your needs.
- Section Organization: The guide is divided into clear sections such as Introduction, Quick Start, Features, FAQ, Known Issues, and Command Summary.
2.2 Sections:
- Installation: Step-by-step setup instructions for InnSync.
- Features: Detailed breakdown of each command with usage examples.
- FAQ & Known Issues: Solutions to common questions and troubleshooting tips.
- Command Summary: A quick-reference table for all available commands.
3. Quick Start
3.1 Installation
Ensure you have Java
17or above installed on your Computer.
Mac users: Ensure you have the precise JDK version prescribed here.Download the latest
.jarfile from here.Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for InnSync.
Open your command terminal, depending on what OS you use follow the instruction below.
- Windows: Tutorial on how to open a terminal here.
- MacOS:Tutorial on how to open a terminal here.
- Linux: Tutorial on how to open a terminal here.
Navigate to the folder by using
cdinto the folder you put the jar file in, and use thejava -jar innsync.jarcommand to run the application.A GUI similar to the below should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app contains some sample data.
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. e.g. typing
helpand pressing Enter will open the help window.
Some example commands you can try:
list: Lists all contacts.add n/John Doe p/+65 98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01: Adds a contact namedJohn Doeto the Address Book.delete 3: Deletes the 3rd contact shown in the current list.clear: Deletes all contacts.exit: Exits the app.
Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
If you are unsure about specific technical terms used in this guide, refer to the Glossary section for definitions.
3.2 Graphical User Interface Layout:
3.2.1 User Interface Overview:
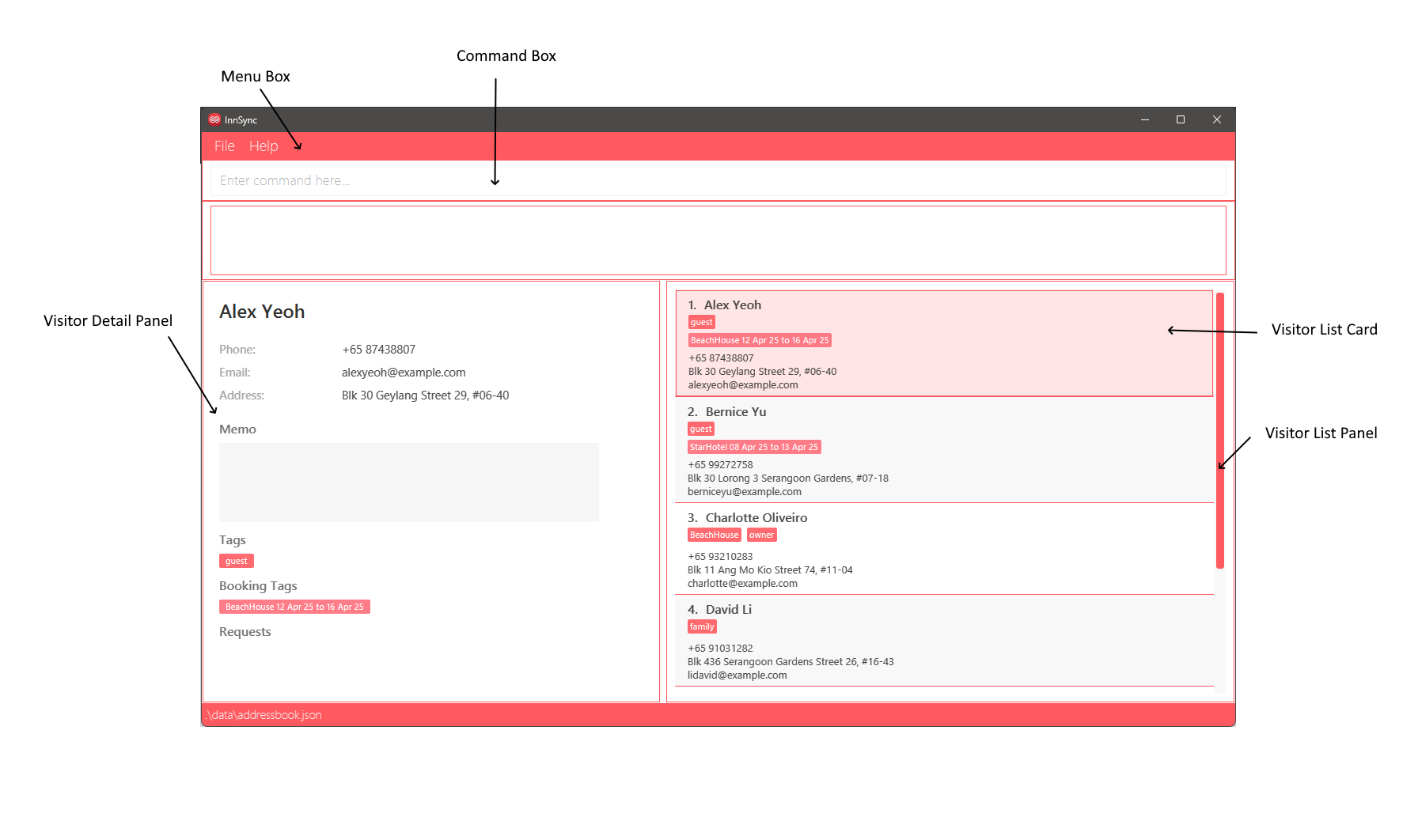
- Menu Box: The menu bar, located at the top of the interface, provides access to various functions and features within InnSync.
- Command Box: This section allows users to enter commands for InnSync to execute.
- Result Box: The box shows the results of executed commands at the interface.
- Visitor List Panel: This panel visually represents the list of visitor in InnSync.
- Visitor List Card: Within the Visitor List Panel, each visitor is depicted with their details displayed in card format.
- Visitor Detail Panel: This panel visually represents the selected visitor in InnSync.
3.2.2 Other UI Components:
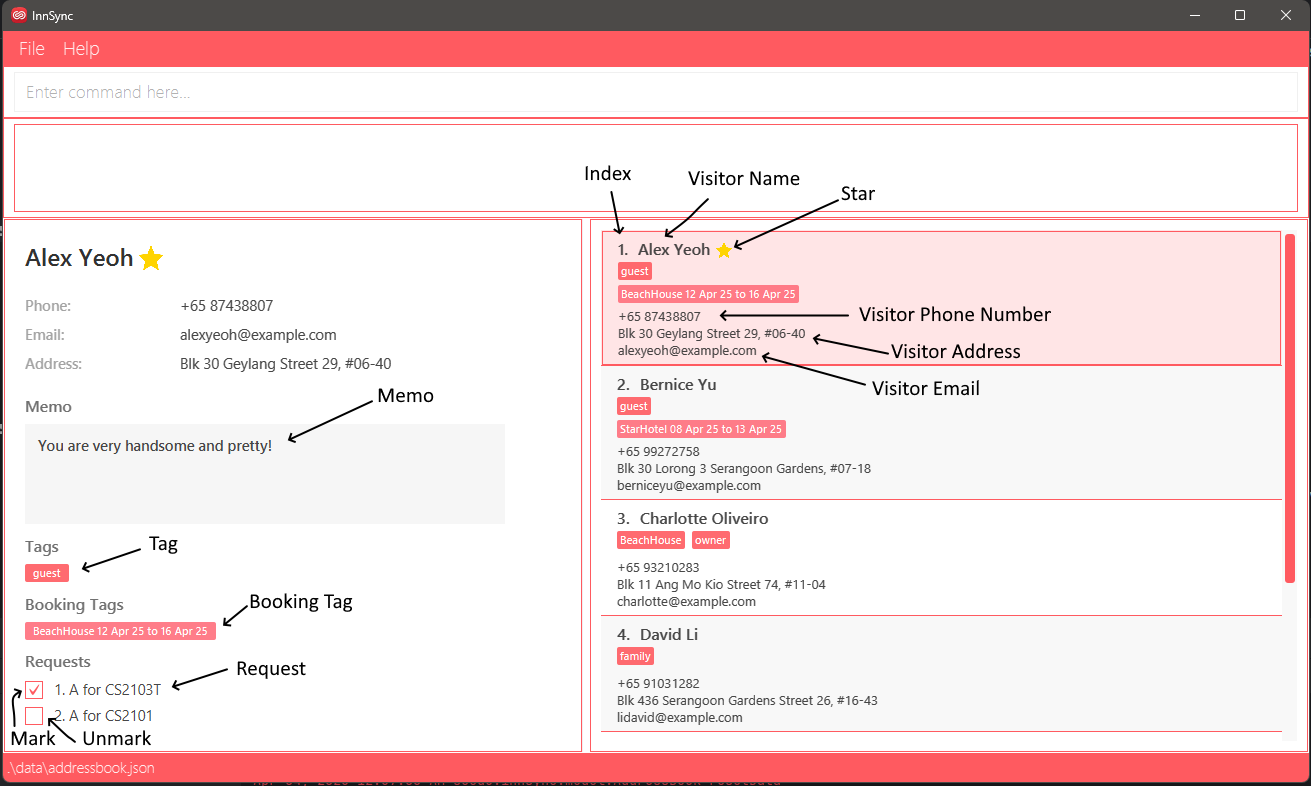
- Index: This component displays the position of each visitor in the Visitor List Panel.
- Visitor Name: The Name is displayed in both the Visitor Detail and Visitor List Panel, which represent the name of the visitor.
- Visitor Phone Number: The contact number associated with the visitor.
- Visitor Address: The physical location or residence of the visitor, which may be used for record-keeping.
- Visitor Email: The email address of the visitor.
- Star: The visitor was starred.
- Memo: A free-text field for storing additional notes or important details about the visitor.
- Tag: Label assigned to a visitor to tag them based on anything.
- Booking Tag: Labels related to the visitor's booking, the dates are represented with
dd-MMM-yy format, but inputted withyyyy-MM-dd. - Request: Special accommodations or preferences requested by the visitor where the user records it.
- Mark: Denote the completion of said request by the user.
- Unmark: Denote the request as not completed.
- Selected Visitor: Highlighted in pink, this component indicates the selected Visitor Detail Panel for viewing.
3.3 How to Use InnSync Features:
InnSync operates mainly through CLI commands. Before exploring to the specific features in details under the feature section. Let's try to familiarize ourselves with the basic components and formats to execute a command.
💡Tip: All the command words are case-sensitive!
addis different fromAdd
3.3.1 Parameter Prefixes:
In InnSync, a parameter prefix acts as a delimiter for specifying different types of parameters in commands. Here's a reference table for all parameter prefixes and their corresponding parameters:
| Parameter Prefix | Corresponding Parameter |
|---|---|
n/ | NAME |
p/ | PHONE |
e/ | EMAIL |
a/ | ADDRESS |
b/ | BOOKING_TAG |
bp/ | BOOKING_PROPERTY |
bd/ | BOOKING_DATE |
t/ | TAG |
r/ | REQUEST |
r/ | REQUEST_INDEX |
m/ | MEMO |
3.3.2 Parameters:
In InnSync, a parameter represents a placeholder where users input data. Parameters typically follow immediately after their corresponding Parameter Prefixes. Essentially, they are to be supplied by the user.
📌Note: All user inputs, including parameters, will be trimmed (all leading and trailing whitespaces will be ignored).
| Parameter | Prefix | Description |
|---|---|---|
NAME | n/ | Specifies the name of a visitor. Requirements:
|
PHONE | p/ | Specifies the phone number of a visitor. Requirements:
Used in Commands: add, edit, and find |
EMAIL | e/ | Specifies the email of a visitor. Requirements:
Used in Commands: add, edit, and find |
ADDRESS | a/ | Specifies the address of a visitor. Requirements:
Used in Commands: add, edit, and find |
BOOKING_TAG | b/ | Specifies the booking tag of a visitor. Requirements:
Used in Commands: add, edit, tag and untag |
BOOKING_PROPERTY | bp/ | Specifies the booking property of a visitor for the feature find.Requirements:
Used in Commands: find |
BOOKING_DATE | bd/ | Specifies the booking date of a visitor for the feature find.Requirements:
Used in Commands: find |
TAG | t/ | Specifies the tag name of a visitor. Requirements:
Used in Commands: add, edit, tag, untag and find |
REQUEST | r/ | Specifies the request of a visitor. Requirements:
Used in Commands: add, edit, req, and deletereq |
REQUEST_INDEX | r/ | Refers to the index number shown in the Request panel. Requirements:
Used in Commands: mark and unmark |
MEMO | m/ | Specifies the memo of a visitor. Requirements:
Used in Commands: add, edit, memo and find |
INDEX | N/A | Refers to the index number shown in the List Panel. Requirements:
Used in Commands: edit, delete, req, deletereq, memo, tag, untag, mark, unmark, star and unstar |
3.3.3 Command Format:
To understand how a full command is interpreted, we will utilise the following example.
Example: add n/NAME p/PHONE e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG...] [b/BOOKING_TAG...] [r/REQUEST...]
💡Tip: You can add a visitor without specifying a tag, booking tag and request and that is why it has a bracket around it!
Structure of Command:
| Component | Description | |
|---|---|---|
add | Command | Executes Add Command to add a visitor. |
n/ | Parameter Prefix | Unique prefix to distinguish NAME from other prefixes. |
NAME | Parameter | Represents placeholder for name of the visitor. |
📌General Notes about InnSync:
A command can be categorized into three formats:
COMMAND+INDEXCOMMAND+PARAMETER_PREFIX+PARAMETERCOMMAND+INDEX+PARAMETER_PREFIX+PARAMETER
📌Notes about the command format:
e.g. in `add n/NAME`, `NAME` is a parameter which can be used as `add n/John Doe`.
Items in square brackets are optional.
e.gn/NAME [t/TAG]can be used asn/John Doe t/friendor asn/John Doe.Items with
... after them can be used multiple times (including zero).
e.g.[t/TAG...]can be used as(i.e. 0 times),t/friend,t/friend t/familyetc.Parameters can be in any order.
e.g. if the command specifiesn/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER, thenp/PHONE_NUMBER n/NAMEis also acceptable.Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
help,list,exitandclear) will be ignored.
e.g. if the command specifieshelp 123, it will be interpreted ashelp.If you are using a PDF version of this document, be careful when copying and pasting commands that span multiple lines as space characters surrounding line-breaks may be omitted when copied over to the application.
4. Features
4.1 Command Summary
| Action | Format and Examples |
|---|---|
| Add Visitor | add n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG...] [b/BOOKING_TAG...] [r/REQUEST...] [m/MEMO] e.g., add n/James Ho p/+82 22224444 e/jamesho@example.com a/123, Clementi Rd, 1234665 t/friend |
| Edit Visitor | edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE_NUMBER] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG...] [b/BOOKING_TAG...] [r/REQUEST...] [m/MEMO] e.g., edit 2 n/James Lee e/jameslee@example.com |
| List Visitor | list |
| Delete Visitor | delete INDEX e.g., delete 3 |
| Star Visitor | star INDEX e.g., star 1 |
| Unstar Visitor | unstar INDEX e.g., unstar 1 |
| List Starred Visitors | liststar |
| Tag Visitor | tag INDEX t/TAG [t/TAG...] e.g., tag 1 t/friend or tag INDEX b/PROPERTY from/yyyy-MM-dd to/yyyy-MM-dd [b/BOOKING_TAG...] e.g., tag 1 b/Hotel from/2025-10-10 to/2025-10-11 |
| Untag Visitor | untag INDEX t/TAG e.g., untag 1 t/friend or untag INDEX b/PROPERTY from/START_DATE to/END_DATE e.g., untag 1 b/Hotel from/2025-10-10 to/2025-10-11 |
| Add Request | req INDEX r/REQUEST [r/REQUEST...] e.g., req 1 r/a request |
| Mark Request | mark INDEX r/REQUEST_INDEX e.g., mark 1 r/1 |
| Unmark Request | unmark INDEX r/REQUEST_INDEX e.g., unmark 1 r/1 |
| Delete Request | deletereq INDEX r/REQUEST_INDEX e.g. deletereq 1 r/1 |
| Memo Visitor | memo INDEX m/[MEMO] e.g., memo 1 m/cool |
| Find | find [n/KEYWORD...] [p/KEYWORD...] [e/KEYWORD...] [a/KEYWORD] [t/KEYWORD...] [bp/KEYWORD...] [bd/KEYWORD...] [m/KEYWORD...]e.g., find n/john n/bob p/879294 |
| Clear | clear |
| Exit | exit |
| Undo | undo |
| Help | help |
4.2 Features Related to Visitors
Visitors are uniquely identified by a combination of their email and phone number. Duplicate visitor contact details are not allowed in the address book.
Suppose this contact exists in the address book:
- Person A - Name:
John Doe, Email:john@example.com, Phone:+65 8888 8888, ...
Then, suppose we would like to add these contacts to the address book:
- Person B - Name:
John Lee, Email:john@example.com, Phone:+65 8888 8888, ... - Person C - Name:
John Lee, Email:johnlee@example.com, Phone:+65 8888 8888, ... - Person D - Name:
John Doe, Email:john@example.com, Phone:+65 9999 9999, ... - Person E - Name:
John Lee, Email:johnlee@example.com, Phone:+65 9999 9999, ...
When the program checks for duplicates,
- Person B is rejected - the email and phone are identical!
- Person C is accepted - the phone may be the same, but the email is different!
- Person D is accepted - the email may be the same, but the phone is different!
- Person E is accepted - both the email and phone are different!
📌Note: Two phone numbers are considered identical as long as they contain the same country code, and their numbers have the same digits in the same order. The position and number of whitespaces are not considered. i.e. +65 8888 8888 is considered the same as +65 88888888.
4.2.1 Adding a visitor: add
Adds a visitor to the address book.
Format: add n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG...] [b/BOOKING_TAG...] [r/REQUEST...] [m/MEMO]
💡Tip: A visitor can have any number of tags or requests (including 0) and at most one memo.
💡Tip: If a visitor's name contains a prefix e.g. /, escape the prefix with $.
e.g. To add a visitor with the name "murthu a/p", use the command add n/murthu $a/p [...].
📌Notes:
- Newly added visitors will be sorted lexicographically among visitors that are not starred
- Each visitor must have a unique email or phone number. e.g. You can't add two visitors with both
alice@gmail.comand+65 87929460.
Examples:
add n/John Doe p/+65 98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01add n/Betsy Crowe t/friend e/betsycrowe@example.com a/Newgate Prison p/+65 1234567 t/criminal t/offence r/cool r/beans m/handsome
4.2.2 Editing a Visitor : edit
Edits an existing visitor in the address book.
Format: edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [b/BOOKING_TAG...] [t/TAG...] [r/REQUEST...] [m/MEMO]
- Edits the visitor specified by
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed visitor list. The index must be a positive integer. - At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- Existing values will be updated to the input values.
- When editing tags, the existing tags of the visitor will be removed i.e adding of tags is not cumulative.
- You can remove all the visitor’s tags by typing
t/without specifying any tags after it. - You can remove all the visitor’s booking tags by typing
b/without specifying any tags after it. - You can remove all the visitor’s requests by typing
r/without specifying any booking tags after it. - You can remove the visitor’s memo by typing
m/without specifying any memo after it.
💡Tip: To edit a visitor's name to contain a prefix, escape the prefix with $.
e.g. To change the name of the first contact in the list to "murthu a/p", use the command edit 1 n/murthu $a/p [...].
Examples:
edit 1 p/+65 91234567 e/johndoe@example.comEdits the phone number and email address of the 1st visitor to be+65 91234567andjohndoe@example.comrespectively.edit 2 n/Betsy Crower t/Edits the name of the 2nd visitor to beBetsy Crowerand clears all existing tags.edit 2 n/Betsy Crower b/Edits the name of the 2nd visitor to beBetsy Crowerand clears all existing booking tags.edit 2 n/Betsy Crower r/Edits the name of the 2nd visitor to beBetsy Crowerand clears all existing requests.edit 2 n/Betsy Crower m/Edits the name of the 2nd visitor to beBetsy Crowerand clears memo.
4.2.3 Listing All Visitors : list
Shows a list of all visitors in the address book. Starred visitors will be shown first, followed by unstarred visitors. Both groups will be sorted lexicographically within their respective groups.
Format: list
📌Note: Any additional text or parameters after the list command will be ignored.
💡Tip: Listing without any visitors added will recommend you to add some.
4.2.4 Deleting a Visitor : delete
Deletes the specified visitor from the address book.
Format: delete INDEX
- Deletes the visitor specified by
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed visitor list. The index must be a positive integer.
Examples:
listfollowed bydelete 2deletes the 2nd visitor in the address book.find Betsyfollowed bydelete 1deletes the 1st visitor in the results of thefindcommand.
4.3 Features Related to Starring Visitors
Starring a visitor allows you to mark them as important. Starred visitors will be shown first when listing all visitors.
4.3.1 Starring a Visitor : star
Stars a visitor in the address book.
Format: star INDEX
- The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed visitor list. The index must be a positive integer.
💡Tip: Use this command to keep track of your favourite or important visitors!
4.3.2 Unstarring a Visitor : unstar
Unstars a starred visitor in the address book.
Format: unstar INDEX
- The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed visitor list. The index must be a positive integer.
4.3.3 Listing All Starred Visitors : liststar
Shows a list of only all starred visitors in the address book.
Format: liststar
4.4 Features Related to Tagging Visitors
4.4.1 Adding a Booking Tag : tag
Adds a booking tag into the visitor in the address book.
Format: tag INDEX b/PROPERTY from/START_DATE to/END_DATE
- Adds the booking tag to the visitor specified by
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed visitor list. The index must be a positive integer. - All the fields must be provided.
- The date format has to match
yyyy-MM-ddexactly. - If a booking tag has dates that overlap with any existing booking tags the visitor already has, the new booking tag will be rejected.
Examples:
tag 1 b/Hotel from/2025-10-10 to/2025-10-11Adds the booking tag to the 1st visitor on the list.tag 1 b/Hotel from/2025-10-10 to/2025-10-11Adding the same booking tag again will be rejected due to overlapping dates.
4.4.2 Adding a Tag : tag
Adds a tag into the visitor in the address book.
Format: tag INDEX t/TAG
- Adds the tag to the visitor specified by
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed visitor list. The index must be a positive integer. - All the fields must be provided.
- When adding a tag that does not exist in the visitor, the tag will be appended to the previous tags.
- When trying to add a tag that already exists in the visitor, the command will be rejected.
📌Note: Tags are case-sensitive, so friend is different from Friend.
Examples:
tag 1 t/friendAdds the tag to the 1st visitor on the list.tag 1 t/friendAdding the same tag again will be rejected due to duplicate tags.
4.4.3 Untagging a Booking Tag : untag
Removes a booking tag on the 1st visitor in the address book.
Format: untag INDEX b/PROPERTY from/START_DATE to/END_DATE
- Removes a booking tag to the visitor specified by
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed visitor list. The index must be a positive integer. - All the fields must be provided.
- The date format has to match
yyyy-MM-ddexactly. - When removing a booking tag that exists in the visitor, the booking tag will be removed.
- When trying to remove a booking tag that does not exist in the visitor, the command will be rejected.
💡Tip: If you want to remove all booking tags from a visitor, use edit INDEX b/ where INDEX is the index of the visitor!
Examples:
untag 1 b/Hotel from/2025-10-10 to/2025-10-11Removes the booking tag with matching booking tag on the 1st visitor in the list if they exist.untag 1 b/Hotel from/2025-10-10 to/2025-10-11After running example above this line, it will throw an error saying this booking tag does not exist.
4.4.4 Untagging a Tag : untag
Removes a tag on the 1st visitor in the address book.
Format: untag INDEX t/TAG
- Removes a tag to the visitor specified by
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed visitor list. The index must be a positive integer - All the fields must be provided.
- When removing a tag that exists in the visitor, the tag will be removed.
- When trying to remove a tag that does not exist in the visitor, the command will be rejected.
💡Tip: If you want to remove all tags from a visitor, use edit INDEX t/ where INDEX is the index of the visitor!
Examples:
untag 1 t/friendRemoves the tag with matching tag on the 1st visitor in the list if they exist.untag 1 t/friendAfter running example above this line, it will throw an error saying this tag does not exist.
4.5 Features Related to Requests
Adds a request to the visitor in the address book. Requests are used to keep track of what the visitor wants or needs. Each request can be marked as completed or incomplete.
4.5.1 Adding a Request: req
Adds a request into the visitor in the address book.
Format: req INDEX r/REQUEST
- Adds the request to the visitor specified by
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed visitor list. The index must be a positive integer. - All the fields must be provided.
- When adding a request that does not exist in the visitor, the request will be appended to the previous requests.
- When trying to add a request that already exists in the visitor, the command will be rejected.
📌Note: Requests are case-sensitive, so want banana is different from want Banana.
Examples:
req 1 r/Want bananaAdds the request to the 1st visitor on the list.req 1 r/Want bananaWill be rejected due to duplicating request own by this visitor.
4.5.2 Marking a Request: mark
Marks a request as completed for a specific visitor in the address book.
Format: mark INDEX r/REQUEST_INDEX
- Marks the request specified by
REQUEST_INDEXfor the visitor atINDEXas completed. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed visitor list. TheINDEXmust be a positive integer. The request index refers to the index number of the request in the visitor's request list. TheREQUEST_INDEXmust be a positive integer. - All the fields must be provided.
- When marking a request that exists in the visitor that is not yet marked, the request will be marked as completed.
- When marking a request that does not exist in the visitor, the command will be rejected.
- When trying to mark a request that is already marked, the command will be rejected.
Examples:
mark 1 r/1Marks the first request of the first visitor on the list as completed if it exists.mark 1 r/1Marking the same request again will be rejected.
4.5.3 Unmarking a Request: unmark
Unmarks a previously marked request for a specific visitor in the address book.
Format: unmark INDEX r/REQUEST_INDEX
- Unmarks the request specified by
REQUEST_INDEXfor the visitor atINDEXas not completed. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed visitor list. TheINDEXmust be a positive integer. The request index refers to the index number of the request in the visitor's request list. TheREQUEST_INDEXmust be a positive integer. - All the fields must be provided.
- When unmarking a request that exists in the visitor that is marked, the request will be unmarked as not completed.
- When unmarking a request that does not exist in the visitor, the command will be rejected.
- When trying to unmark a request that is not marked, the command will be rejected.
Examples:
unmark 1 r/1Unmarks the first request of the first visitor on the list as not completed if it exists.unmark 1 r/1Unmarking the same request again will be rejected.
4.5.4 Deleting a Request: deletereq
Deletes a request from a specific visitor in the address book.
Format: deletereq INDEX r/REQUEST_INDEX
- Deletes the request specified by
REQUEST_INDEXfor the visitor atINDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed visitor list. TheINDEXmust be a positive integer. The request index refers to the index number of the request in the visitor's request list. TheREQUEST_INDEXmust be a positive integer. - All the fields must be provided.
- When deleting a request that exists in the visitor, the request will be removed from the visitor's request list.
- When deleting a request that does not exist in the visitor, the command will be rejected.
Examples:
deletereq 1 r/1Deletes the first request of the first visitor on the list.deletereq 1 r/1If the visitor has no more requests, this command will be rejected.
4.6 Adding a Memo to a Visitor : memo
Adds a memo into the visitor in the address book.
Format: memo INDEX m/MEMO
- Adds a memo to the visitor specified by
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed visitor LIST. The index must be a positive integer. - All the fields must be provided.
- This command will overwrite the existing memo of the visitor if it exists.
Examples:
memo 1 m/recurring customerOverwrites the memo of the 1st visitor on the list.
💡Tip: You can remove a memo with
memo INDEX m/instead of using theeditcommand!
4.7 Features Related to Finding
4.7.1 Locating Visitors: find
Allows users to search for visitors whose details match the specified keywords.
Format: find [n/KEYWORD...] [p/KEYWORD...] [e/KEYWORD...] [a/KEYWORD...] [bp/KEYWORD...] [bd/DATE...][t/KEYWORD...] [m/KEYWORD...]
- At least one prefix with a keyword must be provided.
- Searches are case-insensitive (e.g.,
n/hanswill matchHans). - Searches match by containment (e.g.,
n/hanwill matchHans). - When multiple keywords are provided for a single field type (e.g.,
n/john n/doe), visitors matching ANY of those keywords will be returned. - When multiple field types are specified (e.g.,
n/john p/9123), visitors matching ANY of the specified fields will be returned. - Each keyword is treated as a complete phrase. (e.g.,
n/john doewill not matchjohnordoeseparately and will only matchjohn doeas a whole).
Search Modes:
| Prefix | Field | What You’re Searching | What to Type (Format) |
|---|---|---|---|
n/ | Name | Contact names | Any value (up to 170 characters). In this system, names can contain any characters except $, including prefixes like a/ or e/. However, names containing prefixes, such as murthu a/p vara must be preceded by a $ to avoid the characters a/p from being interpreted as a prefix. All $ characters found in name parameters will be excluded. |
p/ | Phone | Phone numbers | Digits (0 - 9) with an optional + at the beginning |
e/ | Email addresses | Any value with letters, numbers, and special characters:@, ., _, -, +. | |
a/ | Address | Physical addresses | Any value (up to 500 characters). |
bp/ | Booking Property | Property names in bookings | Any value (up to 170 characters). |
bd/ | Booking Date | Dates in bookings | Use the format yyyy-MM-dd (e.g., 2025-01-15). |
t/ | Tag | Contact tags | Any value (up to 170 characters). |
m/ | Memo | Notes or comments | Any value (up to 500 characters). |
Examples:
Searching by name:
find n/John- Finds contacts with "John" in their namefind n/Betsy n/muthu $a/p vara- Finds contacts with either "Betsy" or "muthu a/p vara" in their name
Searching by phone:
find p/9123- Finds contacts whose phone numbers contain "9123"find p/+65 p/9123- Finds contacts whose phone numbers contain either "+65" or "9123"
Searching by email:
find e/@example.com- Finds contacts with email addresses containing "@example.com"find e/gmail.com e/yahoo.com- Finds contacts with email addresses containing either "gmail.com" or "yahoo.com"
Searching by address:
find a/Clementi- Finds contacts with "Clementi" in their addressesfind a/Blk 123 a/Jurong- Finds contacts with either "Blk 123" or "Jurong" in their addresses
Searching by tag:
find t/friend- Finds contacts with tags containing "friend"find t/friend t/family- Finds contacts with tags containing either "friend" or "family"
Searching by memo:
find m/important- Finds contacts with "important" in their memosfind m/call later m/follow up- Finds contacts with either "call later" or "follow up" in their memos
Searching by booking date:
find bd/2024-12-25- Finds contacts with bookings that include December 25, 2024find bd/2025-01-01 bd/2025-02-14- Finds contacts with bookings that include either January 1, 2025 or February 14, 2025
Searching by booking property:
find bp/Beach House- Finds contacts with bookings at properties containing "Beach House"find bp/Villa bp/Resort- Finds contacts with bookings at properties containing either "Villa" or "Resort"
Combining search fields:
find n/John t/friend- Finds contacts with either "John" in their name OR "friend" in their tagsfind n/Alice p/9123 e/example.com- Finds contacts with "Alice" in their name, "9123" in their phone number, or "example.com" in their email
Common Errors:
- Empty keyword: Please provide a keyword after the prefix.
- Exceeding character limits: Ensure keywords don't exceed the maximum length for each field type.
4.8 General Features
4.8.1 Clearing All Visitors : clear
Clears all entries from the address book.
Format: clear
- After executing
clear, the system will ask the user to confirm the action. - Entering
yorYwill clear the address book, while any other input will cancel the command.
4.8.2 Exiting the Program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
4.8.3 Undoing the Last Command : undo
Undoes the last modification to the address book, reverting it to its original state before the last modification.
Commands edit, add, delete, star, tag, untag, req, deletereq, mark, unmark, unstar, memo, and even another undo are all modifications that can be undone.
📌Note: Using the undo command after another undo command will undo the first undo.
Format: undo
4.8.4 Getting Help : help
Shows a message explaining how to access the help page.
Format: help
4.9 Saving the Data
InnSync's address book data is saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
4.10 Editing the Data File
InnSync's address book data is saved automatically as a JSON file [JAR file location]/data/addressbook.json. Advanced users are welcome to update data directly by editing that data file.
⚠️Caution:
If your changes to the data file makes its format invalid, InnSync will discard all data and start with an empty data file at the next run. Hence, it is recommended to make a backup of the file before editing it.
Furthermore, certain edits can cause the InnSync to behave in unexpected ways (e.g., if a value entered is outside the acceptable range). Therefore, edit the data file only if you are confident that you can update it correctly.
5. FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another computer?
A: Install the app on the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous InnSync home folder.
6. Known issues
- When using multiple screens, if you move the application to a secondary screen, and later switch to using only the primary screen, the GUI will open off-screen. The remedy is to delete the
preferences.jsonfile created by the application before running the application again. - If you minimize the Help Window and then run the
helpcommand (or use theHelpmenu, or the keyboard shortcutF1) again, the original Help Window will remain minimized, and no new Help Window will appear. The remedy is to manually restore the minimized Help Window.
7. Glossary
- Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, MacOS
- AirBnB host: An AirBnB host is an individual or business that list their property on the platform for short-term rentals. The host provide accommodations in the forms of apartments, houses or rooms for guests, typically for leisure activities.
- Visitor: Any individual who accesses an AirBnB property, including guests staying at the property, property owners, service providers performing work, or other authorized individuals. Visitors may include cleaners, maintenance personnel, property inspectors, delivery services, and other vendors.
- CLI (Command Line Interface): A text-based interface where users interact with the application with a keyboard typing commands instead of using a graphical user interface.
- JAR: A packed file format used in Java that contains compiled java codes to enable easy distribution, portability and execution that includes libraries and resources to allow the program to function.
- JSON (JavaScript Object Notation): A lightweight data format widely used for storing and exchanging structured data in a human-readable, that is often used in databases and APIs.
- GUI (Graphical User Interface): A visual graphical interface that allows users to interact with the application using various graphical elements like search boxes, buttons, text boxes, and eta.
- Escape: To escape a prefix means to add a
$before the prefix to prevent it from being interpreted as a command prefix. For example, if you want to add a visitor with the name "murthu a/p", you would use the commandadd n/murthu $a/p [...]. - Parser: A parser is a component of the application that interprets and processes user input commands, breaking them down into their respective components (e.g., prefixes, parameters) for further processing.
- Prefix: A prefix is a special character or string of characters that indicates the type of information being provided in a command. For example,
n/is a prefix for the name of a visitor,p/is a prefix for the phone number, and so on. - Parameter: A parameter is a specific piece of information that follows a prefix in a command. For example, in the command
add n/John Doe,John Doeis the parameter for then/prefix. - Command: A command is a specific instruction given to the application to perform a certain action, such as adding a visitor, editing a visitor, or deleting a visitor.